The most Awaited planter fasciitis orthotics
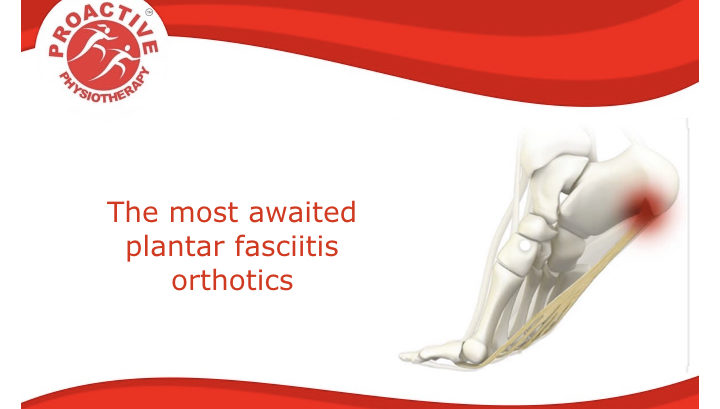
The most common foot pathology is proximal plantar fasciitis, also known as plantar heel pain.
Patients with plantar fasciitis (PF) typically present with plantar heel pain that is worse with the first few steps out of bed or from a seated position. This situation gradually becomes worse with increasing weightbearing activities. On clinical examination, Plantar fasciitis typically presents as tenderness on the medial calcaneal tubercle (i.e. at the origin of the plantar fascia). During gait, patients with more significant PF may exhibit varying levels of heel contact avoidance, increased supination of the subtalar joint (STJ) during midstance and/or a shortened propulsive phase. All of which are central nervous system mediated pain-avoidance mechanisms that the patient may or may not be aware of.
Conservative treatment options that I recommend for PF include the avoidance of barefoot walking and flat shoe/sandals (i.e. low heel height differential), avoidance of running and jumping activities.
The use of gastrocnemius and soleus stretching exercises three times daily, , ice application 1-2 times a day, anti-inflammatory medications, over-the-counter (OTC) foot orthoses. Of course, treatment varies widely for each patient and their particular situation, However,the above treatment options are the most common ones that we recommend.
On average, there is a 50% reduction in the symptoms from PPF within three weeks of the patient receiving their CFOs, even though the individual patient response can vary quite widely.

Our goals for Customise foot orthosis treatment of PF are to relieve the high level of compression and tension stress on the plantar fascia and plantar calcaneus so that the injuries to the tissues of the plantar heel and their symptoms resolve over time. Even though it is commonly believed by many podiatrists that the only cause of PF is excessive tension force within the plantar fascia. The mechanical analysis of the forces and stresses acting at the plantar calcaneus clearly indicate the cause of PF. It is a combination of excessive magnitudes and duration of tension forces within the plantar fascia, excessive magnitudes and duration of compression forces acting directly on the medial tubercle of the plantar calcaneus from ground reaction force (GRF).
The mechanical analyses are also supported by the clinical response of patients with PF to various types of CFO and shoe modifications that reduce these pathological forces. Therefore, it is likely that both of these factors, excessive compression force from GRF and excessive tension force from the plantar fascia, acting together, cause injury to either the plantar fascia itself and/or cause microscopic damage to the osseous structure of the cortical or sub-cortical regions of the plantar calcaneus at the medial calcaneal tubercle.
Specific Customise foot orthosis design recommendations for PF. This foot orthosis help to reducing the compression forces from GRF acting on the plantar heel and reducing the tension forces acting within the plantar fascia during weightbearing activities. To reduce the compression forces acting on the plantar heel, we prescribed the heel cup of the orthosis to be at least 14 mm deep, and most commonly we use a 16 mm deep heel cup in order to spread the GRF acting on the plantar heel.
Consider this…..
The main cause of the patient’s PF is habitual walking on hard surface during the day. we will commonly ask the patient wear orthosis which has 16-18 mm heel cup depth along with only a 1 mm thick lateral heel expansion. This shape of orthosis helps to decrease the radius of curvature of the orthosis heel cup and further transfer more GRF off of the central aspect of the plantar calcaneus. A “plantar heel bubble” may be prescribed into the orthosis to further reduce the painful GRF on the plantar heel .
Medial longitudinal arch (MLA) height and stiffness are also critical to component for successful treatment of PPF with Customise foot orthosis. The MLA of the orthosis must be made sufficiently high and stiff to distribute GRF . However, the MLA of the orthosis must not be so high or stiff that the medial band of the plantar fascia is irritated and/or STJ supination instability is created by the orthosis.

Look for……
If polypropylene orthoses are ordered, we will normally advice a 4 mm (5/32″) plate in patients < 80 kgs or a 5 mm (3/16″) plate in patients > 80 kgs in order to create sufficient medial longitudinal arch stiffness. So that the MLA of the polypropylene orthosis plate does not deform excessively under load, thereby decreasing the therapeutic effectiveness of the CFO. By using these common orthosis modifications, along with careful clinical and biomechanical evaluation of the patient’s foot, excellent results with Customise foot orthosis treatment of PF.
An understanding of the pathomechanics is essential for the patient’s symptoms which helps the clinician to address the needs of the patient more specifically. The material flexibility is more important. A prefabricated orthosis meets some of the needs of all patients. A generic customise foot orthosis meets some of the needs of all pathology. A pathology-specific, custom foot orthosis should meet all the needs of a particular patient with a particular pathology.
Referances:
Kogler G, Veer F, et. al. The influence of medial and lateral placement of orthotic wedges on loading of the plantar aponeurosis, an in vitro study, JBJS AM.81:1403-13,1999
Root M. Development of the functional orthoses, Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Vol 11, No 2, April 1994.
Prescribing Better Foot Orthoses: Proximal Plantar Fasciitis”, December 2009 Foot and Lower Extremity Biomechanics IV: Precision Intricast Newsletters, 2009-2013.
K. B. Landorf and H. B. Menz, “Plantar heel pain and fasciitis,” BMJ Clinical Evidence, vol. 2008, 2008.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!