A sophisticated approach for plantar fasciitis
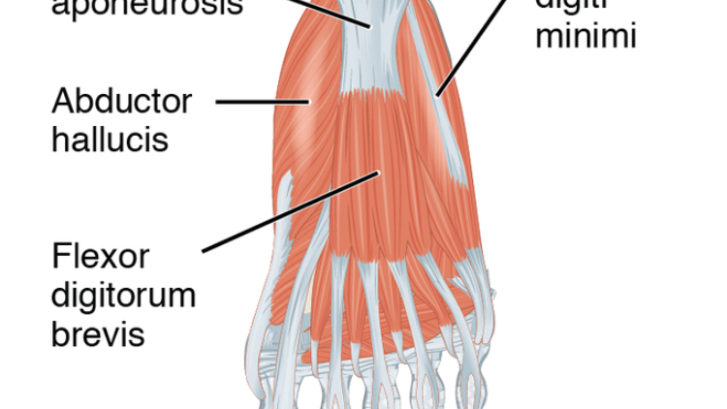
Plantar Fascia is a broad, dense band originating from anterior aspect of calcaneal tuberosity in form of 3 bands namely medial, central and lateral and inserting after dividing into 5 digital bands at metatarsophalangeal joints. It plays vital role in supporting the arch of foot and act as a shock absorber.
Plantar Fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia specifically at the insertion on calcaneal tuberosity.
• This commonly occurs due to overuse injury among those who stand for prolonged period of time or whose activities require maximal plantar flexion of ankle and simultaneous dorsiflexion of MTP joints and long distance runners.
• It even happens among individuals who have pes planus, tight tendo-achilles, weak foot muscles- tibialis posterior, poor shoe support and obesity or sudden weight gain. This typically can happen in absence of windlass mechanism.
Symptoms & signs:
• Swelling at the insertion site
• Temperature rise and redness
• Tenderness at calcaneal tuberosity
• Heel pain that is worse in the morning with the first few steps and exacerbate with climbing stairs. At times it becomes difficult to rest the foot on the floor in the morning. With progression, pain may start interfering with activities of daily living.
Biomechanical alterations due to plantar fasciitis :
• Individuals with flat feet or pronated feet are more prone to develop plantar fasciitis.
• Chronic long standing cases of plantar fasciitis disturbs the windlass mechanism and so individuals with normal arch also start losing flexibility and shock absorbing capacity of foot and it results into collapsing of medial longitudinal arch. This ultimately causes flattening of arch and thereby disturbance in metatarsal break.
• Body being a kinematic chain, any alteration at one joint result into alterations/ compensations at other joints.
• Flattening of medial longitudinal arch causes pronation of the foot, which is combination of talocrural dorsiflexion, calcaneal eversion & forefoot abduction. Following this, to have body in one alignment, there results into talar adduction & plantar flexion, compensatory internal rotation of tibia & femur.
• These internal rotatory forces cause positional mal-tracking of patella which causes lateral gliding of patella. The ilio-tibial band, tensor fascia lata & lateral retinaculum gets tight. This results gradual development of patellofemoral dysfunction & thereby knee pain.
• Tight ilio-tibial band, internal rotation of femur causes imbalance of pelvis and causes pelvic-femoral and sacroiliac dysfunction which results into back pain. This may progress to change biomechanics till cervical region and even atlanto occipital joint.
• Thus in a nutshell foot pain can alter entire biomechanical chain- foot pain can result pain in knee, back and even neck.
How to approach ?
• Rest- till pain subsides in acute cases. Avoid prolonged walking, running and jumping.
• Before initiating weight bearing in morning, patient can be asked to move toes in warm water to lessen the pain.
• Cryotherapy can help reduce pain- 5-10minutes massage or ice pack application for 15-20 minutes; 3-4times daily.
• Needling , myofascial release and deep friction massage over the plantar fascia.
• Plantar Fascia stretching- can be done in different positions- patient/ therapist’s hold the heel of the affected foot with one hand and other hand’s fingers pulling the toes of affected foot into extension at MTP joint.

Woodstown massage:
• Stretching of the tendoachilles- gastrocnemius and soleus with the help of towel or theraband- ankle dorsiflexion with knee in extension for gastrocnemius and ankle dorsiflexion with knee in flexion for soleus. It should be gentle, slow, static & can be done in long sitting or standing- hold time 30-60 secs, 5 reps, 3 times/day.
• Tight fascia can be released by rolling the fascia over a tennis ball or bottle filled with cold water.

Podantics podiatry
• Once the flexibility is gained and its painfree, strengthening exercises of calf and intrinsic foot muscles should be started, as this can prevent reoccurrence and can provide muscular support for weakened plantar fascia.
✓ Toe curling/ towel scrunching exercises: strengthens the intrinsic muscles of foot.  Patient in sitting position with foot flat on the floor with towel placed underneath. Patient is asked to curl the toes to try to lift & pull the towel off the floor with the heel in contact with the floor throughout the exercise- done for 1-2minutes.
Patient in sitting position with foot flat on the floor with towel placed underneath. Patient is asked to curl the toes to try to lift & pull the towel off the floor with the heel in contact with the floor throughout the exercise- done for 1-2minutes.
✓ Calf raises –unilateral & bilateral- 3 times/day for 20 rep in each session.
✓ Short foot exercises/ arch lifts- strengthen the muscles that support the medial longitudinal arch. The patient is asked to draw the metatarsal heads towards the calcaneus without flexing the toes or lifting the ball of great toe & foot, heel off the floor. Hold for 5 secs and relax- 1 minute. Initially done by sitting on chair with foot flat on floor and the gradually progressed in standing. It will require good amount of practice to master.
✓ Toe band exercises for toe muscles strengthening- elastic band is wrapped around all 5 toes. It should be fit yet comfortable. Instruction is given to move the toes apart pulling against the band- 3-5secs hold & relax-10-2-times.

✓ Toe squeezes for toe muscles strengthening- small sponges are placed between each toe. Instruction is given to squeeze the sponge with the toes- 3-5secs hold & relax-10-2-times.
✓ Mobilization can be given- talocrural posterior glide, subtalar lateral glide, anterior & posterior glide of 1st tarsometatarsal joint.
✓ Calcaneal taping may help in temporary reducing pain & function by distributing force away from stressed plantar fascia.
✓ Proper foot wear during daily activities and sports provides good support and prevents plantar fasciitis.
✓ Orthotic devices like Insoles can be used which acts as a soft cushion for heel-12-15mm higher than sole or well molded Achilles pad or heel cuffs or medial longitudinal arch support.
With proper care & physiotherapy, plantar fasciitis patients can become painfree and return to normal activities.
Next Friday post will be on how proximal joint dysfunction can cause plantar fasciitis
Stay tune!!!!
pic courtesy: Wikipedia.org

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!